Pinto Bean Yield With Starter Fertilizer
The NDSU Carrington Research Extension Center (CREC) has been conducting research since 2009 with pinto bean to measure response to phosphorus (P)-based starter fertilizer primarily with liquid 10-34-0 using different application methods and rates. Ten trials were conducted on a well-drained loam soil with 2.6 to 4 percent organic matter and generally low P levels.
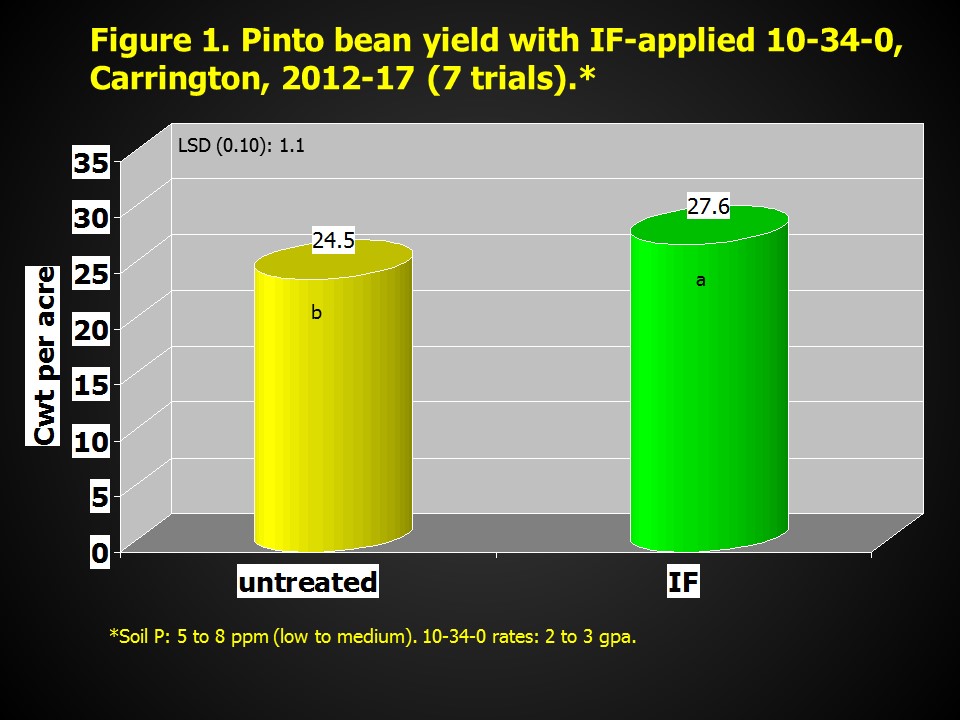
Seed yield averaged across seven trials with in-furrow (IF) -applied 10-34-0 at 2 to 3 gallons per acre (gpa) increased 3.1 hundredweight (cwt) per acre (11 percent), compared with the untreated check (Figure 1). However, plant population was reduced 4 percent with the IF fertilizer application compared to the untreated check. Also, yield was similar between low (2.5 to 3 gpa) and high (5 to 6 gpa) rates of IF-applied 10-34-0. The high fertilizer rate reduced plant population by 13 percent.
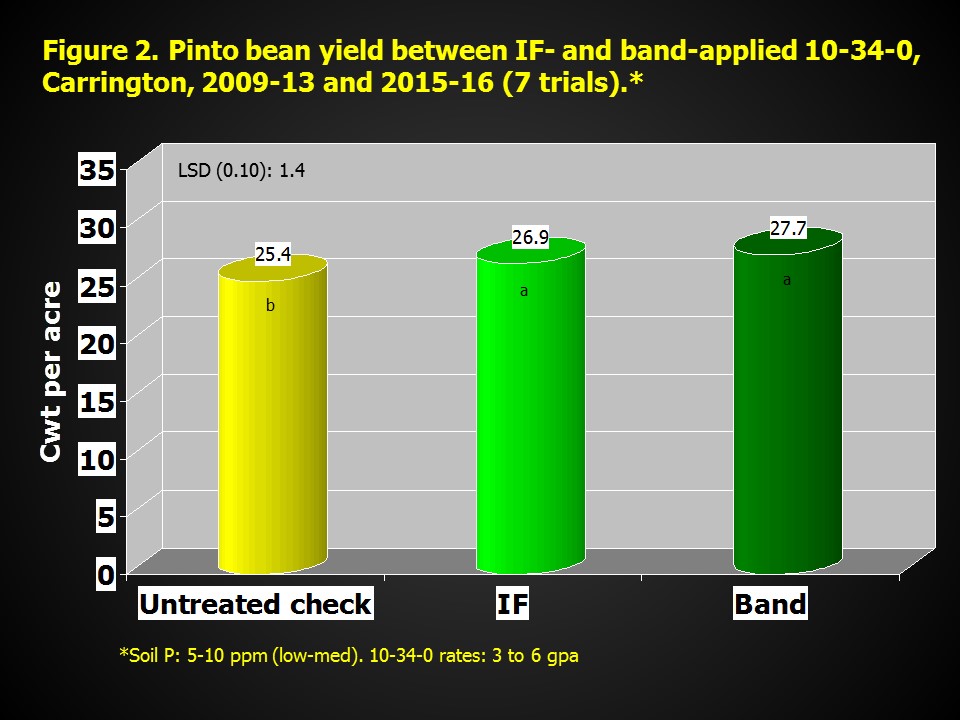
Yield between IF- and band-applied (2 inches from seed) 10-34-0 at 3 to 6 gpa was statistically similar averaged among seven trials (Figure 2). However, the plant population was reduced an average of 13 percent with IF-applied 10-34-0, compared with band-applied 10-34-0 and the untreated check. The banded fertilizer application provides soil separation between fertilizer and bean seed that reduces the risk of seed damage from fertilizer salts and ammonium-nitrogen.
NDSU Extension circular A1883 ‘Pinto bean response to phosphorus starter fertilizer in east-central North Dakota’ contains the previously mentioned results plus additional research summaries. The publication will soon be posted on the web and currently can be obtained by contacting the CREC (701.652.2951).
Greg Endres
Gregory.Endres@ndsu.edu
Extension Agronomy Specialist


