5 Keys to Understanding Your Health Insurance Costs (FS1814, July 2016)
Availability: Web only
 Know Your Health Insurance Terms and Definitions
Know Your Health Insurance Terms and Definitions
Knowing the terms used in talking about health insurance will help you be more comfortable when talking about your health insurance with your medical providers. Knowing the language makes asking questions easier.
Bold text indicates a term also defined in this glossary.
Allowed amount
Maximum amount on which payment is based for covered health-care services. This may be called “eligible expense,” “payment allowance” or “negotiated rate.” If your provider charges more than the allowed amount, you may have to pay the difference. A preferred provider may not charge for the difference.
Balance billing
When a provider bills you for the difference between the provider’s charge and the allowed amount. For example, if the provider’s charge is $100 and the allowed amount is $70, the provider may bill you for the remaining $30. A preferred provider cannot charge you the balance of the bill for covered services.
Coinsurance
Your share of the costs of a covered health-care service, which is calculated as a percent (for example, 20 percent) of the allowed amount for the service. You pay coinsurance plus any deductibles you owe. For example, if the health insurance or plan’s allowed amount for an office visit is $100 and you’ve met your deductible, your coinsurance payment of 20 percent would be $20. The health insurance or plan pays the rest of the allowed amount.
Copayment (copay)
A fixed amount (for example $15) you pay for a covered health-care service, usually when you receive the service. The amount can vary by the type of covered health-care service.
Deductible
The amount you will pay for health-care services your health insurance covers before your health insurance begins to pay. For example, if your deductible is $1,000, your plan won’t pay anything until you’ve met your $1,000 deductible for covered health-care services subject to the deductible. The deductible may not apply to all services.
Deductible is waived
Some health insurance plans waive the deductible for some medical services. For these medical services only, the plan will pay any charges over the amount of the copay, even if the deductible has not been met.
Excluded services
Health-care services that your health insurance or plan doesn’t pay for or cover.
Formulary
A list of prescription drugs, generic and brand name, covered by a prescription drug plan or an insurance plan offering prescription drug benefits.
Nonformulary
Any drug not listed on the formulary. These drugs will not be covered by the health plan’s prescription drug plan.
Health insurance
A health insurance policy is a legally binding contract between the insurance company and the insured. The policy describes how much your health insurer will pay for your health-care costs in exchange for a monthly premium.
In-network coinsurance
The percent (for example, 20 percent) you pay of the allowed amount for covered health-care services to providers who contract with your health insurance or plan. In-network coinsurance usually costs you less than out-of-network coinsurance.
In-network copayment
A fixed amount (for example $15) you pay for covered health-care services to providers who contract with your health insurance or plan. In-network copayments usually are less than out-of-network copayments.
Network
The facilities, providers and suppliers your health insurer or plan has contracted with to provide health-care services.
Nonpreferred provider
A provider who doesn’t have a contract with your health insurer or plan to provide services to you. You’ll pay more to see a nonpreferred provider. Check your policy to see if you can go to all providers who have contracted with your health insurance or plan or if your health insurance or plan has a “tiered” network and you must pay extra to see some providers.
Out-of-network coinsurance
The percent (for example, 40 percent) you pay of the allowed amount for covered health-care services to providers who do not contract with your health insurance or plan. Out-of-network coinsurance usually costs you more than in-network coinsurance.
Out-of-network copayment
A fixed amount (for example $30) you pay for covered health-care services from providers who do not contract with your health insurance or plan. Out-of-network copayments usually are more than in-network copayments.
Out-of-pocket limit
How much you must pay for medical services during a policy period (usually a year) has a limit. Once that out-of-pocket limit has been reached, your health insurance begins to pay 100 percent of the allowed amount for each service. This limit never includes your premium, balance-billed charges or health care your health plan doesn’t cover. Some health plans don’t count all of your copayments, deductibles, coinsurance payments, out-of-network payments or other expenses toward this limit.
Pre-authorization
A decision by your health insurer or plan that a health-care service, treatment plan, prescription drug or durable medical equipment is medically necessary.
Preferred provider
A provider who has a contract with your health insurer or plan to provide services to you at a discount. Check your policy to see if you can see all preferred providers or if your health insurance or plan has a “tiered” network and you must pay extra to see some providers. Your health insurance or plan may have preferred providers who also are “participating” providers. Participating providers also contract with your health insurer or plan, but the discount may not be as great, and you may have to pay more.
Premium
The amount that must be paid for your health insurance or plan. You and/or your employer usually pay it monthly, quarterly or yearly.
Prescription drug coverage
Health insurance or plan that helps pay for prescription drugs and medications.
Provider
A physician (M.D., medical doctor, or D.O., doctor of osteopathic medicine), health-care professional or health-care facility licensed, certified or accredited as required by state law.
Primary care provider
A physician (M.D., medical doctor, or D.O., doctor of osteopathic medicine), nurse practitioner, clinical nurse specialist or physician assistant, as allowed under state law, who provides, coordinates or helps a patient access a range of health-care services.
Summary of benefits
Health Insurance companies must provide you with a short document detailing in plain language information about their health plan benefits and coverage. It will summarize the key features of the plan, such as the covered benefits, cost-sharing provisions, and coverage limitations and exceptions.
Tiers
Within a plan’s formulary list of medications covered, each medication will be placed in a tier, as in Tier 1, Tier 2, etc. Lower-level Tier 1 medications will be less expensive; higher-level tiers will cost you more.
This glossary has many commonly used terms but isn’t a full list. These glossary terms and definitions are intended to be educational and may be different from the terms and definitions in your plan.
 Know Your Network
Know Your Network
Using network health providers saves you money. A network is made of the different health-care providers, including doctors, clinics, hospitals and pharmacies, with whom an insurance company has contracts to deliver health-care services at negotiated fees.
When selecting a health insurance plan, one of the most important features to consider is the network.
What Is a network?
A network is made up of the different health-care providers with whom an insurance company has contracts to deliver health-care services at negotiated fees. Most insurers contract with all types of providers: physicians, surgeons, therapists, hospitals, pharmacies and labs, to name the most common.
Who is in your network?
Your insurance company will provide you with a list of all of the current providers in its network. Reviewing the list of network providers is important to see if the doctors, hospitals and other health-care providers you already see for health care, or would like to see for health care, are on that list.
Your health plan also may have a preferred network and a nonpreferred network of providers. The plan may provide more cost assistance with the preferred network, although you still can choose a nonpreferred provider and pay a higher portion of the cost.
In-network vs. out-of-network
If a provider is under contract, that provider is considered “in-network.” If the provider is not under contract, that provider is considered “out-of-network.”
How does a network work?
The most important difference between using an in-network provider and an out-of-network provider is cost. Many insurance plans encourage you to use in-network providers by offering lower deductible, coinsurance and copay amounts when you use network providers.
That does not mean that you cannot use other providers. But if you do choose to use an out-of-network provider, the insurance plan’s share of the costs will be less than if you used an in-network provider. You will pay more for services. Some health plans may not cover any of the costs when you see an out-of-network provider. Use in-network providers to keep your health-care costs lower.
When you call to make an appointment, ask if the provider is still in your insurance plan’s network.
What about seeing a specialist?
Some plans instruct you to visit a primary-care provider (usually an internist or a family doctor) before seeking a consultation from a specialist. In those plans, the primary-care provider is the one who gives you a formal referral to a specialist if you need specialty care. A visit to a specialist may have a higher copay or coinsurance. Also determine if the specialist is in-network or out-of-network.
What if I travel a lot during the year?
Because most networks feature local health-care providers, you will be faced with an added out-of-network expense if you need medical care while you travel. Some plans allow you to use out-of-network providers in a medical emergency. Ask your insurance provider how it handles medical expenses incurred when you travel away from home.
Source: This material was adapted from a publication authored by Elizabeth Kiss, Ph.D., et al., Finding a Network Provider, Fact Sheet, Kansas State University, April 2015.
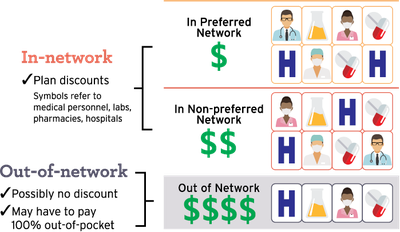
Image adapted from: Health Insurance Literacy for the Marketplace, 2014
 Know Your Costs
Know Your Costs
The four types of costs you may pay when using health insurance are premiums, deductibles, copayments and coinsurance. You need to be aware of what they are and how and when they are paid.
Premium
If your plan has a premium, you or your employer must prepay your premium each month. For example, the January premium is paying for February’s health insurance coverage. If you don’t pay your premium every month, you will lose your health insurance. Make sure to pay on time every month. Keep records of each payment.
Deductible
Your deductible is an amount of money you have to pay for health services you use each year. After you have paid your deductible, your health insurance will pay its share for any other health services you need during the year. Some of the health services you may have to pay for until you reach your deductible are doctor visits, lab ork or a visit to the emergency room. Your health plan also may waive the deductible for some services. You do not have to pay anything for services that are preventive, such as flu shots and birth control.*
Copay
The copay is a fixed amount you pay when you get a health service that is not preventive. A health service could be a doctor visit, a laboratory test, a prescription medicine or a visit to the emergency room.
Different types of health services have different copays. For example, a doctor’s office visit may have a $25 copay. You must pay this at the doctor’s office.
Your copay for prescription drugs could be $15 for some medicines and more for others. You must pay this copay at the drug store.

Coinsurance
After you have paid your deductible for the year, you may have to pay coinsurance for certain health services that are not preventive.
This charge is a part or percentage of the total cost for these health services.
Here’s an example: Sonya has a deductible of $1,000 and coinsurance of 20 percent. After she paid her deductible for the year, she had an accident and needed an X-ray. The X-ray cost $100. Her insurance paid $80 and she paid $20.
Out-of-Pocket Limits
All qualified health insurance plans now must have an out-of-pocket limit. This is the most you pay during a policy period (usually a year) before your health insurance or plan begins to pay 100 percent of the allowed amount. This limit never includes your premium, balance-billed charges or health care your health insurance or plan doesn’t cover. Some health insurance or plans don’t count all of your copayments, deductibles, coinsurance payments, out-of-network payments or other expenses toward this limit.
Source: Adapted from My Health My Voice publication developed by Raising Women’s Voices for the Health Care We Need.
* Some health insurance plans were grandfathered into the Affordable Care Act regulations and may not cover all of these preventive-care services at no cost. Check with your insurance provider to determine if it is a grandfathered plan.
 Know Your Preventive Care
Know Your Preventive Care
“Preventive care” is regular health care intended to keep you healthy and avoid disease. Many preventive health-care services are fully covered by your health insurance plan at no cost to you.
Preventive services that are no additional cost to you with your health insurance*:
For women only
Well-woman visits
Birth control
Test for cervical cancer
Tests and counseling for sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis and HPV
Mammograms (after age 40)
Osteoporosis tests (after age 60)
Help if you are the victim of domestic violence
Tests during pregnancy for anemia, gestational diabetes, hepatitis B, Rh incompatibility, urinary tract infections
Breastfeeding support, counseling and supplies
Folic acid supplements
Breast cancer genetic test counseling (BRCA)
Breast cancer chemoprevention counseling
For adults
Tests
Blood pressure
Cholesterol
Colorectal cancer (after age 50)
Depression
Diabetes (Type 2) test (if you have high blood pressure)
Hepatitis B (if you have higher risk)
Hepatitis C (if you have higher risk)
HIV
Lung cancer (if you are a heavy smoker aged 55-80)
Vaccines
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Influenza (flu)
HPV
Measles, mumps, rubella (German measles)
Meningitis
Pneumonia (pneumococcal)
Shingles
Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough)
Chicken pox
Weight loss counseling (if you are obese)
Diet counseling (if you have high risk of disease)
Help for alcohol abuse
Help quitting smoking (smoking cessation)
For children
Autism screening
Behavioral assessments
Blood pressure screening
Cervical dysplasia screening
Depression screening
Developmental screening
Dyslipidemia screening
Fluoride chemoprevention supplements
Gonorrhea preventive medication
Hearing screening
Height, weight and body mass index measurements
Hemoglobin screening
Sickle cell screening
HIV screening
Hypothyroidism screening for newborns
Immunization vaccines
Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis
Hemophilic influenza Type B (Hib)
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Human papillomavirus
Inactivated poliovirus
Influenza (flu)
Measles, mumps, rubella
Meningococcal
Pneumococcal
Rotavirus
Varicella
Iron supplements for children
Lead screening for children at risk of exposure
Medical history for all
Obesity screening and counseling
Oral health risk assessment
Phenylketonuria (PKU) screening
Sexually transmitted infection (STI) prevention counseling and screening for adolescents at higher risk
Tuberculin testing for children
*Some health insurance plans were grandfathered into the Affordable Care Act regulations and may not cover all of these preventive-care services at no cost. Check with your insurance provider to determine if it is a grandfathered plan.
 Know Your Prescription Drug Coverage
Know Your Prescription Drug Coverage
All qualified health insurance plans include a prescription drug benefit plan. These benefits can help in paying for prescription drugs your family uses. Each health plan covers prescription drugs differently. Know your plan!
Prescription drugs
Medications that are prescribed by a doctor to treat an illness or condition. “Over the counter” (OTC) drugs usually are not covered, even if a doctor writes you a prescription for them.
The Basics of Prescription Drug Coverage
Each health insurance plan has a list of covered medicines called the formulary. Each health plan may have different medications in its formulary. The formulary lists each brand and generic name of medicines that the plan includes. Formularies can change. Medicines can be added or removed.
If your doctor prescribes a medication that is not on your health plan’s formulary list, you will be responsible for the entire cost of that medication.
Formularies may have two or more cost levels, called tiers. The copayment and/or coinsurance for each tier will be different. Higher-level tiers cost you more. For instance, a third-tier medicine will cost you more than a first-tier one.
Many health plans have three or four tiers of costs:
- Tier 1: Generic medicines, which cost the least
- Tier 2: Preferred, brand-name medicines
- Tier 3: Nonpreferred, brand-name medicines
- Tier 4: Specialty medicines, which often are costly, brand-name medicines
Your prescription benefits may have a copay and/or a coinsurance that you are responsible for when purchasing a medication. Your health plan’s summary of benefits will tell you if you have a copay and coinsurance and how much they are. Your health insurance card also may list your prescription co-pay.

Note: You may have a separate deductible for prescription drugs. You may need to pay it as well as a deductible for medical services. Look at your health plan’s summary of benefits about prescription medicines to see what you are responsible for paying.
Contact your health insurance provider for a list of medications in your health plan’s formulary.
Additional resources
Federal Government Health Insurance Exchange
A Woman’s Step-by-Step Guide to Using Health Insurance
Understanding Health Insurance
Sources
Elizabeth Kiss, Ph.D., et al., Finding a Network Provider, Fact Sheet, Kansas State University, April 2015.
My Health, My Voice, A Woman’s Step-By-Step Guide to Using Health Insurance, The 4 Kinds of Costs you May Pay, November 2015.
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2012). Glossary of Health Coverage and Medical Terms.
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2012). Sample Summary of Benefits and Coverage.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Preventive Services Covered Under the Affordable Care Act. Retrieved April 2016.
JULY 2016

